Spring Security 是 Spring 官方建議使用的 Authentication Framework。它的強大是眾所皆知,但它的複雜卻是惡名昭彰。Spring Security 幾乎將所有的元件都抽象化,以至於無法直覺地了解。本章將深入淺出探討 Spring Security 的架構。其他完整的細節,請參考 Spring Security 的官方文件。
Table of Contents
Spring Security 與 Servlet
在了解 Spring Security 的架構之前,先讓我們來看一下,Spring Security 是如何在 Servlet 的架構下運作。下圖顯示,當一個 HTTP request 進來時,Servlet 和 Spring Security 的處理流程。
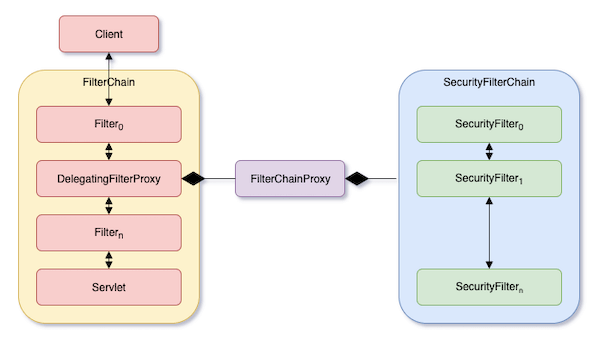
圖中左邊,Client Application 送出一個 HTTP request,進入 Servlet 的 FilterChain,最後到達 Servlet。在 Spring 中,這個 Servlet 會是 DispatchServlet。
FilterChain 裡的每一個 Filter 都會對自己的下一個 Filter 呼叫 Filter.doFilter(),如下方的程式碼:
public class FilterX implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) {
// Do something before
filterChain.doFilter(request, response, filterChain);
// Do something after
}
}DelegatingFilterProxy
Spring 提供一個叫 DelegatingFilterProxy 的 Filter。它是 Servlet 和 Spring 的 ApplicationContext 中間的橋樑。Spring Security 在 Servlet 的 FilterChain 中安插一個 DelegatingFilterProxy,然後在這個 DelegatingFilterProxy.doFilter() 裡,它從 ApplicationContext 中取出 FilterChainProxy Bean,並呼叫 FilterChainProxy.doFilter(),如下方的程式碼。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) {
Filter delegate = getFilterBean("FilterChainProxy");
delegate.doFilter(request, response, filterChain);
}DelegatingFilterProxy 可以說是,從 Servlet 的世界正式進入 Spring 的世界。而,FilterChainProxy 可以說是,從 Spring 的世界進入 Spring Security 的世界。
FilterChainProxy & SecurityFilterChain
FilterChainProxy 是 Spring Security 提供的。FilterChainProxy 裡包含一個 List<SecurityFilterChain>,而這些 SecurityFilterChain 都是 Bean。當一個 HTTP request 進到 FilterChainProxy 後,它會對每個 SecurityFilterChain,呼叫 SecurityFilterChain.matches(request)。然後對回傳 true 的那一個,呼叫 SecurityFilterChain.getFilters(),以取得在 SecurityFilterChain 裡的 List<Filter>。
不過取得的是 List<Filter>,而不是一個 FilterChain,所以利用 VirtualFilterChain 把 List<Filter> 弄的像 FilterChain 一樣。最後就是呼叫 VirtualFilterChain.doFilter()。
過程的程式碼大致如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) {
List<Filter> filters = this.getFilters();
if (filters == null) {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
VirtualFilterChain vfc = new VirtualFilterChain(request, filterChain, filters);
vfc.doFilter(request, response);
}
private List<Filter> getFilters(HttpServletRequest request) {
for (SecurityFilterChain chain : this.filterChains) {
if (chain.matches(request)) {
return chain.getFilters();
}
}
return null;
}FilterChainProxy 裡包含 List<SecurityFilterChain> 而不是單獨一個 SecurityFilterChain,主要是讓它可以根據 HTTP request,選擇特定的 SecurityFilterChain 來處理。
Security Filters
SecurityFilterChain.getFilters() 回傳的是 List<Filter>。這些 Filter 都是 Spring Security 提供的 Filter,所以我們稱這些 Filter 為 Security Filter。
Spring Security 已經有一套預設的 SecurityFilterChain。我們將介紹在這預設的 SecurityChain 中的很後面兩個 Security Filter – ExceptionTranslationFilter 和 FilterSecurityInterceptor。
Spring Security Authentication 基本流程
ExceptionTranslationFilter
下圖顯示 ExceptionTranslationFilter 的邏輯。
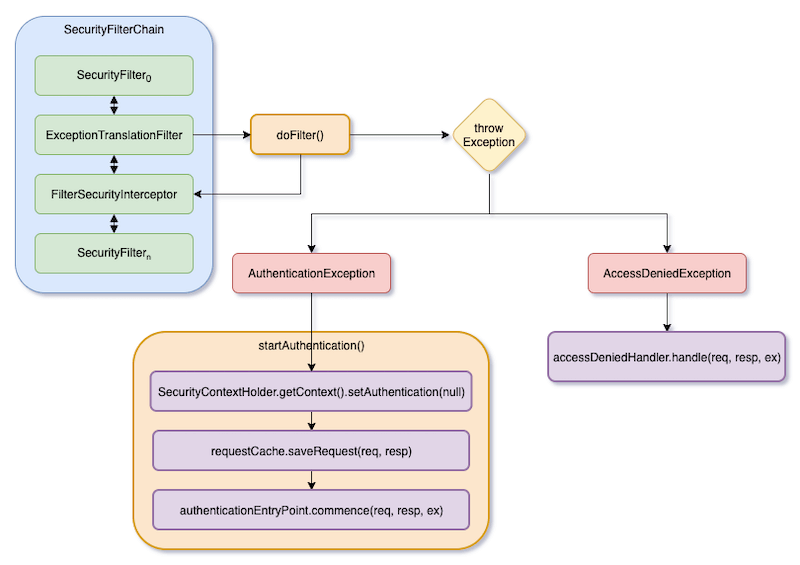
若是用程式碼來看上圖邏輯的話,大致如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) {
try {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (AccessDeniedException | AuthenticationException e) {
if (!isAuthenticated || e instanceof AuthenticationException) {
startAuthentication(request, response, filterChain, e);
} else {
accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response, e);
}
}
}
protected void startAuthentication(
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) {
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}簡單來說,ExceptionTranslationFilter 會直接呼叫它的下一個 Security Filter – FilterSecurityInterceptor,然後 Catch Exception。如果沒有任何 Exception 丟出,那 ExceptionTranslationFilter 等於是沒有做任何事情。
若是有 Exception 丟出,而且是 AuthenticationException 的話,那就會啟動請求 Authentication 的流程。所以它會先清空 SecurityContext 裡面的 Authentication,再呼叫 authenticationEntryPoint.commence() 來向 Client 請求 Credentials。
若是 AccessDeniedException,那就會呼叫 accessDeniedHandler.handle()。
最後會直接 return,則這個 HTTP request 就不會到 DispatchServlet 那邊了。
AuthenticationEntryPoint
AuthenticationEntryPoint 是在 startAuthentication() 的最後面。所以它是被設計用來向 Client 請求 Credentials。我們來看看幾個例子。
BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint
BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint 是用在 Basic Authentication 的情況。它在 response 中寫入 WWW-Authenticate,讓 Client 可以在下一個 HTTP request 做 Authentication。
public class BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint, InitializingBean {
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) {
response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=\"" + realmName + "\"");
response.sendError(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(), HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.getReasonPhrase());
}
}LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint
LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint 是用在 Login Form 的情況。它會重新導向到登入頁,讓 Client 輸入 Username 和 Password 來登入。
public class LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint, InitializingBean {
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) {
response.sendRedirect(loginUrl);
}
}Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint
Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint 是用在,當你不想要向 Client 請求 Credentials,而只想要直接回傳錯誤的情況下。如果你是用 Bearer token 的話,那這可能就是你要的。而且如果你的 API 是 RESTful 的話,那就會想要回傳 JSON 字串。
public class Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN, "Access Denied");
}
}AccessDeniedHandler
AccessDeniedHandler 是用來處理當 HTTP request 被拒絕的情況,如因權限不足而被拒絕。
AccessDeniedHandlerImpl 會重新導向到 403 頁面,或是直接寫入 response。如果你的 API 是 RESTful 的話,那就會要回傳 JSON 字串。
public class AccessDeniedHandlerImpl implements AccessDeniedHandler {
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
if (errorPage != null) {
request.setAttribute(WebAttributes.ACCESS_DENIED_403, accessDeniedException);
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value());
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(errorPage);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
} else {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value(), HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.getReasonPhrase());
}
}
}SecurityContextHolder
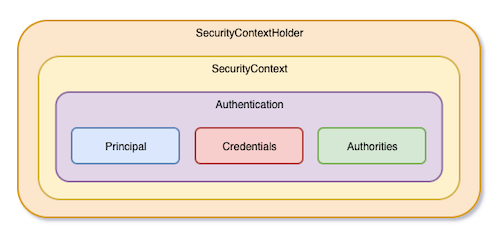
SecurityContextHolder 是 Spring Security 用來儲存驗證過的 Authentication,結構大致如下圖所示。
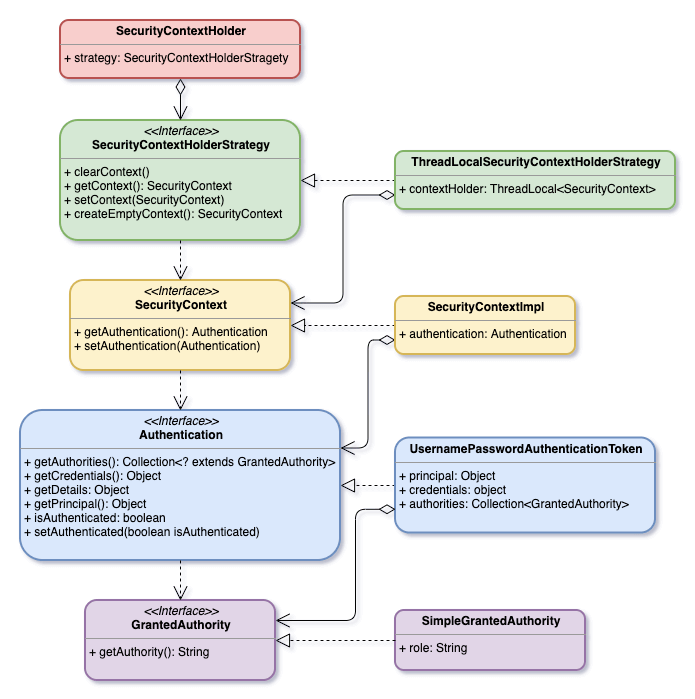
除了 SecurityContextHolder 是 class 之外,其餘全部是都是 interface。下圖用 UML 呈現它們的關係,並且各挑出一個實作的 class,以易於了解。
在我們探討每一個 interface 之前,先來了解一下,如何使用 SecurityContextHolder。使用方法很直接,就是直接將驗證過的 Authentication 設定到 SecurityContextHolder。它是 static,所以設定之後,整個程式可以透過 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() 來取得驗證過的 Authentication。如果回傳 null,表示沒有被驗證過。
Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(request.username, request.password); Authentication authenticated = authenticationManagerBuilder.object.authenticate(authentication); SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticated);
SecurityContextHolderStrategy
SecurityContextHolderStrategy 是用來決定要怎麼儲存 SecurityContext。
例如 GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy 是讓整個程式共用一份 SecurityContext。
class GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy implements SecurityContextHolderStrategy {
private static SecurityContext contextHolder;
}而 ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy 是讓每一個 Thread,有自己的一份 SecurityContext。而這也是 Spring Security 預設的 SecurityContextHolderStrategy。所以在 Spring Boot 中,每一個 HTTP request 都是一個 Thread 在處理。那也就是說,每一個 HTTP request 都有自己的一份 SecurityContext。
class ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy implements SecurityContextHolderStrategy {
private static final ThreadLocal<SecurityContext> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
}SecurityContext
SecurityContext 主要就是包含一個驗證過的 Authentication 物件。
Authentication
Authentication 主要包含 Principal、Credentials、和 Authorities,這三樣東西。其中 Principal 和 Credentials 會因為不同的 Authentication,而有不同的定義,所以它們才會宣告為 Object。
例如,Principal 常常會是登入時的 Username,而 Credentials 則是登入時的 Password。若是用 Token 時,那 Credentials 就可能會是 Token。
GrantedAuthority
GrantedAuthority 是用在 Authorization 階段。權限是用字串定義的,所有的權限字串都有前綴 ROLE_。
例如,下方的程式碼設定 GET /greet 必須要有 ROLE_ADMIN 的權限。在呼叫 .hasRole() 時,裡面的字串要去除 ROLE_。
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/greet").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
}
}應此在產生 Authentication 的時候,就要給定 ROLE_ADMIN 權限,這樣這個 HTTP request 才可以存取 GET /greet。如下方的程式碼所示:
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList();
authorities.add(SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"));
Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(request.username, request.password, authorities);
Authentication authenticated = authenticationManagerBuilder.object.authenticate(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticated);AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager 是用來驗證 Authentication 物件的。驗證過後的 Authentication 才會被設定到 SecurityContextHolder。ProviderManager 是最常用的 AuthenticationManager 實作。它裡面有一個 List<AuthenticationProvider>,每個 AuthenticationProvider 都有機會去驗證傳進去的 Authentication。當沒有任何的 AuthenticationProvider 可以驗證這個 Authentication 的話,那它就會用 parent 來去驗證。若還無法驗證,那 ProviderManager 就會丟出 AuthenticationException。
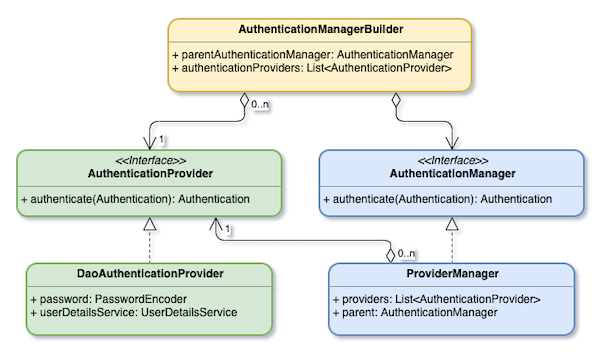
DaoAuthenticationProvider 是一個 AuthenticationProvider 的實作。它是用來做 Username/Password 模式的驗證。
另外,在程式中要取得預設的 AuthenticationManager 實例的話,要透過 AuthenticationManagerBuilder。因為 AuthenticationManagerBuilder 是一個 Bean。下面的程式碼顯示如何使用 AuthenticationManagerBuilder。
@Autowire private AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationManagerBuilder; Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password); Authentication authenticated = authenticationManagerBuilder.getObject().authenticate(authentication); SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticated);
Spring Security Authorization 基本流程
Authentication 通過後,接下來就是 Authorization 的流程。FilterSecurityInterceptor 這個 Security Filter 就是在處理這個流程。
FilterSecurityInterceptor
FilterSecurityInterceptor 的基本流程如下圖:
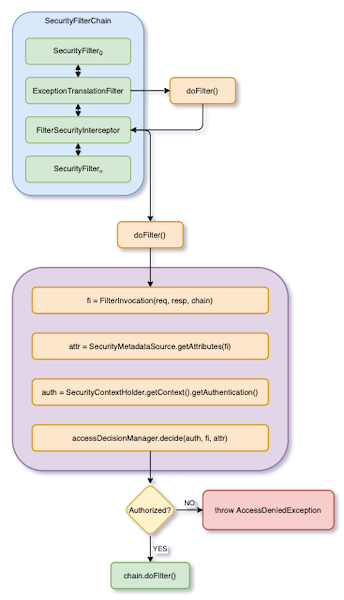
上圖的邏輯,大致上如下面的程式碼:
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, filterChain);
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(fi);
Authentication authenticated = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
try {
accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, fi, attributes);
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
throw e;
}FilterSecurityInterceptor 做的事情主要是,根據傳進來的 HTTP request 取得 Collection<ConfigAttribute>。然後,將 Collection<ConfigAttribute> 以及驗證過的 Authentication 傳給 AccessDecisionManager,以決定是否授權這個 Authentication 來存取這個 Resource。
例如,下面的程式碼中,設定 GET /greet 需要 ROLE_ADMIN 的權限。
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/greet").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
}
}但是,FilterSecurityInterceptor 中取得的 Authentication 裡面的 authorities 只有 ROLE_USER。
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList();
authorities.add(SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(request.username, request.password, authorities);
Authentication authenticated = 這樣根據這個 HTTP request 中請求的 Resource GET /greet ,所取得的 Collection<ConfigAttribute> 會有一個 ConfigAttribute,而它裡面會是 hasRole(‘ROLE_ADMIN’)。這時 accessDecisionManager.decide() 會發現,GET /greet 這個 Resource 需要 hasRole(‘ROLE_ADMIN’) 權限,但是取得的 Authentication 裡面的 authorities 只有 ROLE_USER 權限,因此會丟出 AccessDeniedException。
結語
Spring Security 提供了一個高度可擴充的架構。你可以依據系統的需求,客製化一套符合系統的驗證流程。不過,也因為過度的抽象化,使得複雜度大大地提升。希望在閱讀本章之後,可以讓你對 Spring Security 有一定的了解。












1 comment
謝謝, 非常清楚易懂.