Android activity 和 fragment 都有自己的 lifecycle。整個 lifecycle 中包含了數個 callbacks。了解它們的 lifecycles 以及那些 callbacks 有助於我們撰寫出強健的程式。本文章將介紹 activity 和 fragment 的 lifecycles。
Table of Contents
Activity Lifecycle
一般來說,一個 activity 實作一個 screen。大部分的 apps 包含了多個 screens,也就是說 apps 包含了多個 activities。在 Android 的四個 application components 中,activity 應該是我們最常用到的一個。
Activity class 提供了數個 lifecycle callback methods,系統藉由呼叫它們來通知 activity 的狀態改變了。因此我們必須了解這些 lifecycle callbacks 代表什麼意義,以及何時會被系統呼叫。這樣子我們才可以實作出強健的程式碼。
下圖顯示 activity 的 lifecycle。
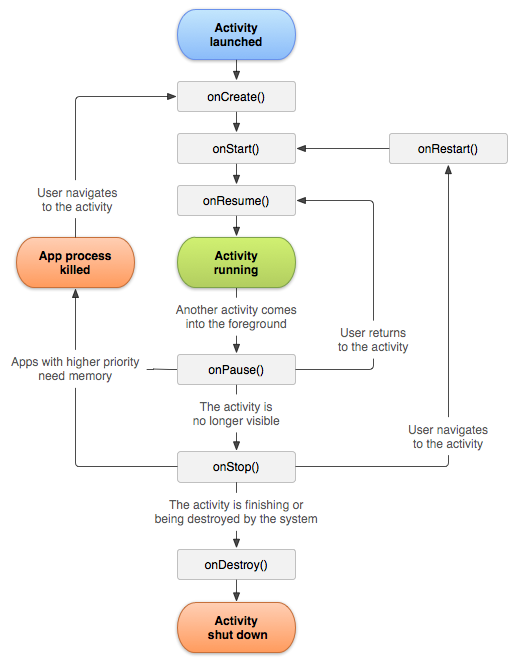
下圖顯示 activity lifecycle states 和 events。

下表列出,在每一個 lifecycle callback 裡,我們應該做什麼事,更詳細的內容請參照 Activity lifecycle。
| Callback | Lifecycle.State | Lifecycle.Event | 何時被呼叫 | 應該做什麼 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| onCreate() | CREATED | ON_CREATE | 當系統建立 activity 時 | onCreate() 只會在 activity 的整個 lifecycle 中被執行一次。 實作 activity 的 startup 邏輯程式碼。例如,綁定 data 到 lists,初始化 class-scope 變數。 |
| onStart() | STARTED | ON_START | 當 activity 是 visible | 初始化維護 UI 的程式碼。 |
| onResume() | RESUMED | ON_RESUME | 當 activity 進入 foreground | 此時 Activity 可以和 user 互動。 初始化會在 onPause() 中被停止的功能或被釋放的 system resources。 |
| onPause() | STARTED | ON_PAUSE | 當 activity 離開 foreground | 此時 activity 不在 foreground,但還是 visible。 停止不再需要的功能和釋放 system resources。例如,停止 camera preview。 |
| onStop() | CREATED | ON_STOP | 當 activity 不再是 visible | 由於 activity 是 invisible,停止不再需要的功能、釋放 system resources、和將資料儲存資料庫。例如,停止 animations。 |
| onDestroy() | DESTROYED | ON_DESTROY | 當 activity 將要被銷毀 | 釋放所有還沒被釋放的 resources。 |
乍看之下,我們似乎可以在 onStart() 或 onResume() 中實作維護 UI 的程式碼。但是它們還是有些微的差別。
在 single-window mode 下,screen 只會顯示一個 window,也就是一個 activity。大部分手機都是此模式。所以當 activity 離開 foreground 時,常常意味著當前的 activity 是 invisible。不過,當有一個半透明的 activity 顯示時,當前的 activity 是不在 foreground,但依然是 visible。
在 multi-window mode 下,screen 可以同時顯示多個 windows,也就是多個 activities。例如,screen 可以在左半邊顯示 Google Map app,而在右半邊顯示 Chrome app。若當前的 focus 是在 Google Map app 上,而我們將 focus 切換到 Chrome app 上時,Google Map app 當前的 activity 是不在 foreground 但還是 visible。
Fragment Lifecycle
Fragment 是可重複使用的 UI 元件。一個 activity 可以顯示多個 fragments。Fragment 也有自己的 lifecycle。
下圖顯示 fragment 的 lifecycle 和它的 view 的 lifecycle。

State transitions 有兩個方向,分別是 Upward state transitions 和 Downward state transitions。它們呼叫 callbacks 和發送 events 的順序不一樣。

下表列出,在每一個 lifecycle callback 裡,我們應該做什麼事,更詳細的內容請參照 Fragment lifecycle。
| Callback | Fragment State | Fragment Event | View State | View Event | 何時被呼叫 | 應該做什麼 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| onAttach() | 當 fragment 被加入至 FragmentManager 和它的 host activity | |||||
| onCreate() | CREATED | ON_CREATE | 當 fragment 被建立,並且 onAttach() 已被呼叫 | 從 savedInstanceState 回覆之前儲存的資料。 | ||
| onCreateView() | CREATED | INITIALIZED | 當 fragment 要建立它的 view 時 | Inflate 或建立 fragment 的 view。 | ||
| onViewCreated() | CREATED | INITIALIZED | 當 fragment 的 view 已經建立時 | 初始化維護 view 和開始觀察 LiveData。 | ||
| onViewStateRestored() | CREATED | CREATED | ON_CREATE | 當 onStart() 被呼叫之前 | 回覆之前儲存的 view state。 | |
| onStart() | STARTED | ON_START | STARTED | ON_START | 當 fragment 是 visible | 初始化維護 UI 的程式碼。 |
| onResume() | RESUMED | ON_RESUME | RESUMED | ON_RESUME | 當 fragment 進入 foreground | 此時 fragment 可以和 user 互動。初始化會在 onPause() 中被停止的功能或被釋放的 system resources。 |
| onPause() | STARTED | ON_PAUSE | STARTED | ON_PAUSE | 當 fragment 離開 foreground | 此時 fragment 不在 foreground,但還是 visible。 停止不再需要的功能和釋放 system resources。 |
| onStop() | CREATED | ON_STOP | CREATED | ON_STOP | 當 fragment 不再是 visible | 由於 fragment 是 invisible,停止不再需要的功能和釋放 system resources。 |
| onSaveInstanceState() | CREATED | CREATED | 當 onStop() 被呼叫後 | 儲存 instance state。 | ||
| onDestroyView() | CREATED | DESTROYED | ON_DESTROY | 當 fragment 的 view 已經從 window 中 detached | 此時是 view 的 lifecycle 的終點。釋放所有參照到 view 的 references,以讓 view 可被 garbage collected。 | |
| onDestroy() | DESTROYED | ON_DESTROY | 當 fragment 被從 FragmentManager 中移除,或 FragmentManager 被銷毀 | 此時是 fragment 的 lifecycle 的終點。 | ||
| onDetach() | 當 fragment 被從它的 host activity 中移除 | |||||
ViewModel Lifecycle
在 MVVM 中,ViewModel 扮演著重要的角色。它包含了 UI state,而且 activity 和 fragment 也透過它去存取 business logic。
ViewModel 的 lifecycle 直接和它的 scope 綑綁在一起。它會 scope 至一個 ViewModelStoreOwner。它會一直處在 memory 中直到它 scope 的 ViewModelStoreOwner 消失。這可能會發生在以下的情況:
- Activity:當它 finishes。
- Fragment:當它 detaches。
- Navigation entry:當它被從 back stack 中移除。
下圖顯示 Activity 和 ViewModel 的 lifecycle 的關係圖。這也可以應用在 Fragment 和 ViewModel 的關係。
值得注意的是,我們常常會在 onCreate() 中請求 ViewModel。但是 onCreate() 可能會因為 configuration change(如 rotate screen)而被呼叫多次。ViewModel 只有第一次被請求時會被建立,並且一直存在,直到 activity 被 destroyed。

當 Configuration Change 時
有一些事件會觸發 configuration change,如 rotate screen、改變 language 等。當 configuration change 發生時,activity 會被銷毀並重新建立。更詳細的內容請參照 Configuration change occurs。

當從 Activity 切換到新的 Activity 時
我們從 activity 切換到一個新的 activity,且新的 activity 是完全覆蓋 screen 時,它們的 state changes 如下。

當按下 Back 時
當 activity 在 foreground,而使用者按下 Back 按鈕時,activity 的 state changes 如下。在 activity 被銷毀時,它也會被從 back stack 中移除。
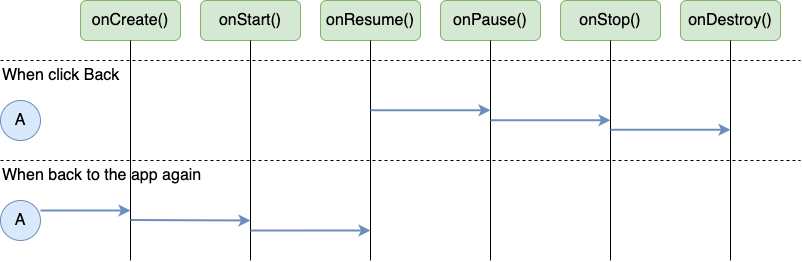
當按下 Home 時
當 activity 在 foreground,而使用者按下 Home 按鈕時,activity 的 state changes 如下。在按下 Home 之後,app 會進入 background。app 當前的 activity 有可能會因為 low memory 被系統終止。

當 Low Memory 發生時
Android 系統會因為需要釋放 RAM,它可能會終止一些 activities。下表顯示,當系統需要終止 activities 時,它會先從哪些 activities 開始。
| Likelihood of being killed | Process state | Final activity state |
|---|---|---|
| Least | Foreground (having or about to get focus) | Resumed |
| Fewer | Visible (no focus) | Started / Paused |
| More | Background (invisible) | Stopped |
| Most | Empty | Destroyed |
結語
Android 有不少元件都有自己的 lifecycle。清楚地了解每個元件的 lifecycle,在正確的時間點做正確的事情,才能夠寫出強健的 app。
參考
- Activity lifecycle, Google developers.
- Fragment lifecycle, Google developers.
- ViewModel overview, Google developers.










