Monotonic stack is a stack in which the value of the elements inside must be increasing or decreasing.
Table of Contents
Monotonic Stack
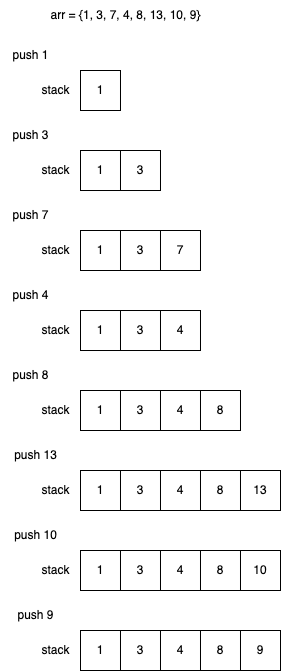
The following algorithm generates an increasing monotonic stack. Whenever it is about to push a value x into the stack, it first checks whether the top value of the stack is greater than x, and if so, pop the top value. In this way, it repeatedly checks the value until the top value is less than x, and then pushes x into the stack. Finally, the resulting stack is increasing.
Algorithm IncreasingMonotonicStack(arr) {
stack := Stack();
for i in arr {
while stack.isNotEmpty && stack.peek() > i {
stack.pop();
}
stack.push(i);
}
return stack;
}The following algorithm will generate a decreasing monotonic stack.
Algorithm DecreasingMonotonicStack(arr) {
stack := Stack();
for i in arr {
while stack.isNotEmpty && stack.peek() < i {
stack.pop();
}
stack.push(i);
}
return stack;
}Example